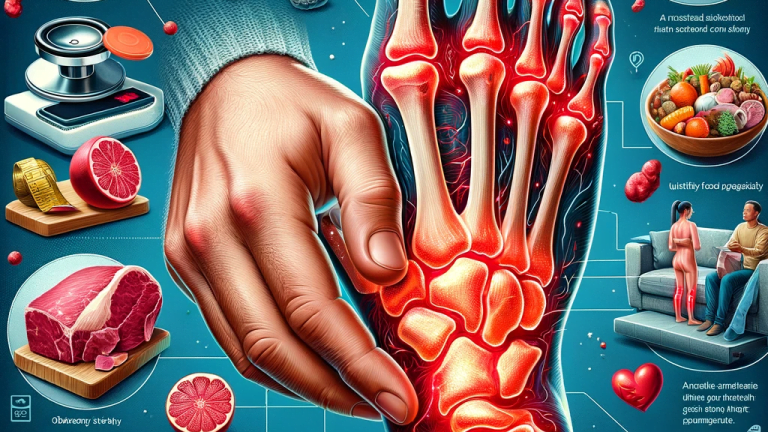
Gout and arthritis are often mentioned together because they share several risk factors and underlying causes. Both conditions cause significant discomfort and affect millions worldwide. Understanding their interconnectedness can help in their management and prevention.
What is Gout?
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to severe pain and swelling. It is often characterized by sudden, intense attacks, typically affecting the big toe.
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is a broader term that encompasses over 100 conditions affecting the joints and surrounding tissues. The most common form is osteoarthritis, where joint cartilage wears down over time.
Shared Risk Factors and Causes
Diet
Both gout and certain types of arthritis can be influenced by diet. Foods high in purines, like red meat and seafood, can increase uric acid levels, exacerbating gout. Similarly, a diet high in processed foods and sugars can contribute to inflammation, worsening arthritis symptoms.
Obesity
Excess weight puts additional strain on the joints, which can exacerbate arthritis symptoms. Obesity also increases the risk of developing gout, as it can lead to increased production of uric acid and decreased renal excretion.
Age and Gender
Age is a significant risk factor for both conditions. Arthritis is more common in older adults, while gout typically affects men over 30 and postmenopausal women.
Genetics
A family history of either gout or arthritis can increase one’s risk, suggesting a genetic predisposition to these conditions.
Lifestyle Factors
Excessive alcohol consumption, particularly beer, can increase the risk of gout. A sedentary lifestyle can exacerbate arthritis symptoms and contribute to obesity, a risk factor for both conditions.
Medical Conditions
Chronic diseases like hypertension and diabetes can increase the risk of developing both gout and arthritis.
Managing and Preventing Gout and Arthritis
Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management, are crucial. Medications may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation or to lower uric acid levels in the case of gout.
Conclusion
Understanding the shared risk factors and causes of gout and arthritis is essential for effective management and prevention. With lifestyle modifications and appropriate medical care, it is possible to manage these conditions effectively.